Identifying the Intermolecular Forces Between Atoms Ions and Molecules
The phase in which a substance exists depends on the relative extents of its intermolecular forces IMFs and the kinetic energies KE of its molecules. Intra molecular forces are those within the molecule that keep the molecule together for example the bonds between the atoms.
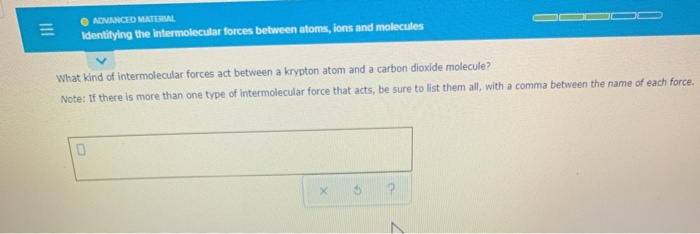
Solved Adnanced Material Identifying The Intermolecular Chegg Com
Inter molecular forces are the attractions between molecules which determine many of the physical properties of a substance.
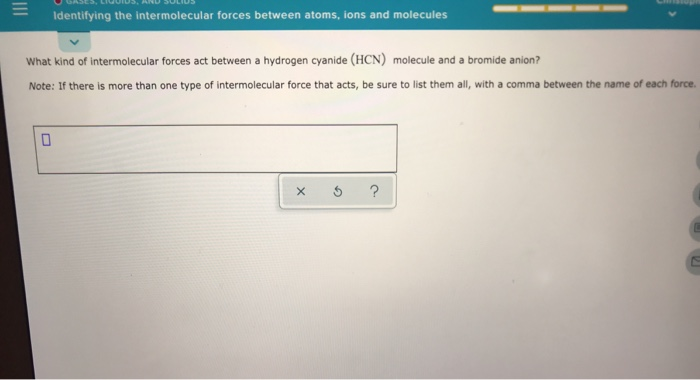
. When a solid state chemical system. When intermolecular forces are strong the atoms molecules or ions are strongly attracted to each other and draw closer together. These forces include dipole-dipole interactionsion-dipole interactions ion-induced dipole interactions van der Waals forces and hydrogen bonding.
These forces are weak compared to the intramolecular forces such as the covalent or ionic bonds between atoms in a molecule. Remember the prefix inter means between. Various physical and chemical properties of a substance are dependent on this force.
This means that ionic forces are interactions which occur between charged atoms or molecules. It occurs in ionic molecules where the ionic bond is formed by the complete transfer of valence electrons between atoms. A type of chemical bond that generates two oppositely charged ions.
The boiling point of a substance is proportional to the strength of its. Chemistry questions and answers. If there is more than one type of intermolecular force that acts be sure to list them all with a comma between the name of each force.
As a result of these differences there are significant differences in the strengths of the resulting attractions. What kind of intermolecular forces act between two carbon tetrachloride molecules. Intermolecular forces hold multiple molecules together and determine many of a substances properties.
The phase in which a substance exists depends on the relative extents of its intermolecular forces IMFs and the kinetic energies KE of its molecules. Ionic bond complete transfer of valence electrons between atoms. This video is my attempt at providing a simple but in-depth explanation of this ALEKS Chemistry topic as I walk you through the steps necessary to solve the.
Here are some tips and tricks for identifying intermolecular forces. IMFs are the various. While ionic and covalent bonds form between atoms intermolecular forces or intermolecular attractions hold molecules together.
Intermolecular Forces are forces that form between molecules atoms or ions 1. The phase in which a substance exists depends on the relative extents of its intermolecular forces IMFs and the kinetic energies KE of its molecules. Steps for Identifying the Strongest Types of Intermolecular Forces.
Positively charged ions are called cations and negatively charged ions are called anions. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Ions Dipoles and Polarizability Concept Overview.
IMFs are the various. The primary difference between bonds and intermolecular forces is the locations of the areas of charge and the magnitudes of the areas of charge. So these are forces between molecules or atoms or ions.
Mechanisms for attaching atoms to one another. Intermolecular forces IMF also known as secondary forces are the forces of attraction that exist between molecules. However to break the covalent bonds between the hydrogen and chlorine atoms in one mole of HCl requires about 25 times more energy430 kilojoules.
The differences in the properties of a solid liquid or gas reflect the strengths of the attractive forces between the atoms molecules or ions that make up each phase. In ammonia there exists a hydrogen bond between the lone pair electrons of nitrogen of one ammonia molecule and the. These are more likely to be found in condensed states such as liquid or solid.
1 illustrates these different molecular forces. This charge is permanent in nature and it is caused by either an excess of electrons in anions or protons in cations. When intermolecular forces are weak the atoms molecules or ions do not have a strong attraction for each other and move far apart.
Dispersion forces induced dipole-dipole forces dipole-dipole forces and hydrogen bonding. The differences in the properties of a solid liquid or gas reflect the strengths of the attractive forces between the atoms molecules or ions that make up each phase. IMFs are the various.
Start studying Identifying the intermolecular forces between atoms ions and molecules. The differences in the properties of a solid liquid or gas reflect the strengths of the attractive forces between the atoms molecules or ions that make up each phase. An intermolecular force is an attractive force that arises between the positive components or protons of one molecule and the negative components or electrons of another molecule.
In Chemistry 101 you learned that ions are simply molecules possessing a charge--anions are negatively charged and cations are positively charged. The first type which is the weakest type of intermolecular force is a London Dispersion force. So these are intermolecular forces that you have here.
Identifying the intermolecular forces between atoms ions and molecules. These forces are required to determine the physical properties of compounds. These are the most prominent intermolecular forces acting in water.
The differences in the properties of a solid liquid or gas reflect the strengths of the attractive forces between the atoms molecules or ions that make up each phase. If there is more than one type of intermolecular force that acts be sure to list them all with a comma between the. Also notice that in the ball and stick models a dashed line is used to identify the intermolecular attractive force between molecules.
Look for the presence of highly electronegative atoms such as O. Covalent bond This bond is formed between atoms that have similar electronegativitiesthe affinity or desire for electrons. Figure 105 Intramolecular forces keep a molecule intact.
The phase in which a substance exists depends on the relative extents of its intermolecular forces IMFs and the kinetic energies KE of its molecules. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. Intermolecular forces are the forces of attraction or repulsion which act between neighboring particles atoms molecules or ions.
Draw the Lewis structure for each molecule. IMFs are the various. We will investigate four types of intermolecular forces.
However the hydrogen bonding intermolecular attractive forces between molecules is stronger compared to the dipole dipole intermolecular attractive forces between molecules. In water there exists a hydrogen bond between the electronegative oxygen of one water molecule and the δ hydrogen atom of another water molecule. ADVANCED MATERIAL Identifying the intermolecular forces between atoms ions and molecules K What kind of intermolecular forces act between a chloroform CHCI molecule and a chloride anion.
Use your textbook andor the Internet to learn about each type.

Aleks Identifying The Intermolecular Forces Between Atoms Ions And Molecules Youtube
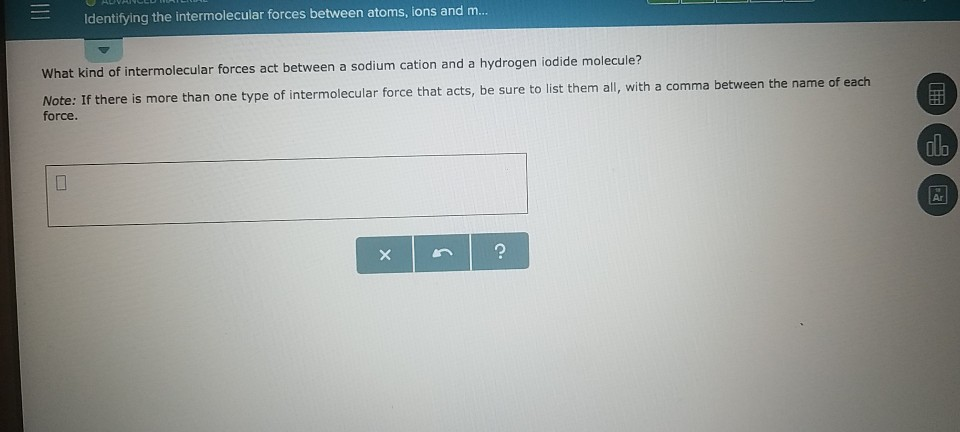
Solved Identifying The Intermolecular Forces Between Atoms Chegg Com
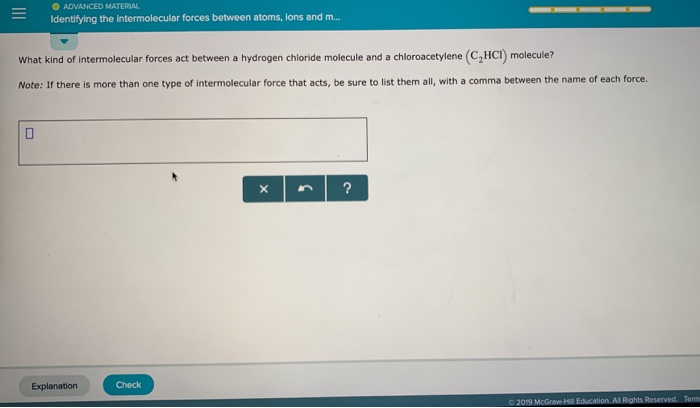
Solved Oadvanced Material Identifying The Intermolecular Chegg Com

Solved Identifying The Intermolecular Forces Between Atoms Chegg Com
No comments for "Identifying the Intermolecular Forces Between Atoms Ions and Molecules"
Post a Comment